DATABASE is a system intended to organize, store, and retrieve large amounts of data easily. It consists of an organized collection of data for one or more uses, typically in digital form. One way of classifying databases involves the type of their contents, for example: bibliographic, document-text, statistical. Digital databases are managed using database management systems, which store database contents, allowing data creation and maintenance, and search and other access.
THE ADVANTAGES of database is Reduced data redundancy, Reduced updating errors and increased consistency, Greater data integrity and independence from applications programs, Improved data access to users through use of host and query languages, Improved data security, Reduced data entry, storage, and retrieval costs, Facilitated development of new applications program.
THE DISADVANTAGES of database is Database systems are complex, difficult, and time-consuming to design, Substantial hardware and software start-up costs, Damage to database affects virtually all applications programs, Extensive conversion costs in moving form a file-based system to a database system, Initial training required for all programmers and users.
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
structure of DBMS:
DBMS (Database Management System) acts as an interface between the user and the database. The user requests the DBMS to perform various operations (insert, delete, update and retrieval) on the database. The components of DBMS perform these requested operations on the database and provide necessary data to the users. The various components of DBMS are shown below:
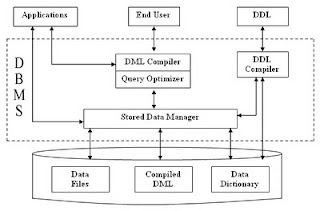
1. DDL Compiler - Data Description Language compiler processes schema definitions specified in the DDL. It includes metadata information such as the name of the files, data items, storage details of each file, mapping information and constraints etc.
2. DML Compiler and Query optimizer - The DML commands such as insert, update, delete, retrieve from the application program are sent to the DML compiler for compilation into object code for database access. The object code is then optimized in the best way to execute a query by the query optimizer and then send to the data manager.
3. Data Manager - The Data Manager is the central software component of the DBMS also knows as Database Control System.
The Main Functions Of Data Manager Are:
Convert operations in user's Queries coming from the application programs or combination of DML Compiler and Query optimizer which is known as Query Processor from user's logical view to physical file system,
Controls DBMS information access that is stored on disk,
It also controls handling buffers in main memory,
It also enforces constraints to maintain consistency and integrity of the data,
It also synchronizes the simultaneous operations performed by the concurrent users,
t also controls the backup and recovery operations.
4. Data Dictionary - Data Dictionary is a repository of description of data in the database. It contains information about
Data - names of the tables, names of attributes of each table, length of attributes, and number of rows in each table, Relationships between database transactions and data items referenced by them which is useful in determining which transactions are affected when certain data definitions are changed, Constraints on data i.e. range of values permitted, Detailed information on physical database design such as storage structure, access paths, files and record sizes, Access Authorization - is the Description of database users their responsibilities and their access rights, Usage statistics such as frequency of query and transactions.Data dictionary is used to actually control the data integrity, database operation and accuracy. It may be used as a important part of the DBMS.5. Data Files - It contains the data portion of the database.
6. Compiled DML - The DML complier converts the high level Queries into low level file access commands known as compiled DML.
7. End Users -
DBMS MODEL
-The hierarchical data model organizes data in a tree structure. There is a hierarchy of parent and child data segments.
-implies that a record can have repeating information, generally in the child data segments. Data in a series of records, which have a set of field values attached to it. It collects all the instances of a specific record together as a record type. These record types are the equivalent of tables in the relational model, and with the individual records being the equivalent of rows.
-example, an organization might store information about an employee, such as name, employee number, department, salary. The organization might also store information about an employee's children, such as name and date of birth.
- The popularity of the network data model coincided with the popularity of the hierarchical data model.
- The basic data modeling construct in the network model is the set construct. A set consists of an owner record type, a set name, and a member record type. A member record type can have that role in more than one set, hence the multiparent concept is supported. An owner record type can also be a member or owner in another set.
- The data model is a simple network, and link and intersection record types (called junction records by IDMS) may exist, as well as sets between them . Thus, the complete network of relationships is represented by several pairwise sets; in each set some (one) record type is owner (at the tail of the network arrow) and one or more record types are members (at the head of the relationship arrow). Usually, a set defines a 1:M relationship, although 1:1 is permitted.
- The CODASYL network model is based on mathematical set theory
- A database based on the relational model developed by E.F. Codd.
- allows the definition of data structures, storage and retrieval operations and integrity constraints. In such a database the data and relations between them are organised in tables. A table is a collection of records and each record in a table contains the same fields.
- Certain fields may be designated as keys, which means that searches for specific values of that field will use indexing to speed them up. Where fields in two different tables take values from the same set, a join operation can be performed to select related records in the two tables by matching values in those fields. Often, but not always, the fields will have the same name in both tables.
-example, an "orders" table might contain (customer-ID, product-code) pairs and a "products" table might contain (product-code, price) pairs so to calculate a given customer's bill you would sum the prices of all products ordered by that customer by joining on the product-code fields of the two tables. This can be extended to joining multiple tables on multiple fields.
- based on the Relational Algebra.
Object-Oriented Model
- add database functionality to object programming languages.bring much more than persistent storage of programming language objects.
- extend the semantics of the C++, Smalltalk and Java object programming languages to provide full-featured database programming capability, while retaining native language compatibility.
- benefit of this approach is the unification of the application and database development into a seamless data model and language environment. As a result, applications require less code, use more natural data modeling, and code bases are easier to maintain. Object developers can write complete database applications with a modest amount of additional effort.
- According to Rao (1994), "The object-oriented database (OODB) paradigm is the combination of object-oriented programming language (OOPL) systems and persistent systems. The power of the OODB comes from the seamless treatment of both persistent data, as found in databases, and transient data, as found in executing programs."


0 ulasan:
Post a Comment